(2 Chronicles 7:14)
Author: Alban Fejza
“So submit yourselves to God. Resist the devil, and he will flee from you.”
(James 4:7)
How to Add the Prayer Times Webpage as an iPhone Icon?
After opening the webpage in Safari, tap the bottom center button:

Then, tap “Add to Home Screen”:
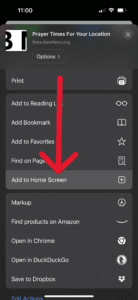
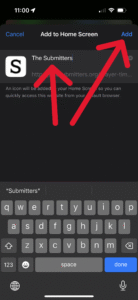
Then, type “The Submitters” and tap “Add”:
The icon should appear somewhere in one of your home screens:

How to Add the Prayer Times Webpage as an Android Phone Icon?
After having the webpage opened in Google chrome,
tap the three dots on top right corner:
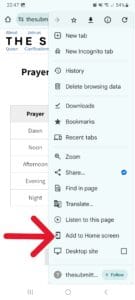
Then tap “Add to Home screen”:
Then type “The Submitters” and then tap “Add”:
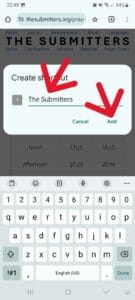
Then tap “Add”:
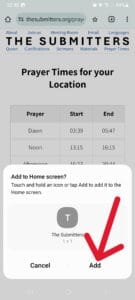
The icon should appear somewhere in one of your home screens:

Is Bank Interest Prohibited in the Quran?
Praise be to God! There is no other god except God.
In Sura 3, verse 130, God prohibits us to engage in what is called “riba”. Let me give you an example what “riba” is. Let’s say that I live in the 15th century, in one of the medieval kingdoms, and I go to a friend, and I tell him that I need 100 gold coins as a loan for a year. He says, “Yes, you can have them, but at the end of the year you have to return 107 gold coins” Now, this is “riba”, prohibited interest – and it literarily means “increase”, and in this case we can see that my friend increased the number of gold coins which I have to return to him compared to what he gave me. And this is prohibited in the Quran.
Now, let’s take another example. Let’s say that I don’t live in the 15th century, but I live today in a democratic country, in Canada for example, and instead of going to my friend, I go to the bank to get a loan of 100,000 dollars, and the bank tells me. “OK, but at the end of the year, you have to return 107,000 dollars.” Now, the question is, “Is this also riba?” Before we answer that, let’s first list the differences between these two examples:
| Example 1 | Example 2 |
| In a kingdom | In a democracy |
| Loan from a human being | Loan from a bank (organisation) |
| Loan in gold coins | Loan in fiat money (paper money which is not backed by gold or silver) |
Now, do these three differences mean that the second example is not an example of ribba (prohibited interest), or is it still prohibited interest (riba)? Let’s analyze it.
So, as we can see, the second example happens in a democracy. But what does it mean to live in a democracy. Democracy in Greek means, “people rule”. So, in a democracy, we do not serve the government, like you do in a kingdom (where you serve the king). In a democracy, the government serves us, which means that the decisions of the government are ultimately a shared responsibility of us, the people in that country. Now, in democracies of today, on behalf of the people, the parliament creates a central bank, which prints money. So, we the people, in a democracy have ordered our servants, the state, more specifically, the central bank, to print money. And guess what, the central bank, as ordered by the parliament, which represents us, distributes that money through other banks by giving it to them as a loan with interest. So, effectively, we the people in democracies have charged interest on the banks first, before they did it to us. And in addition, we the people, listening to our naive economists have authorized the states to print about 2, 3 or 4% of money more than it is needed every year, which they call “inflation”, and this additional printing of money out of thin air is technically stealing from those who have the money – the banks in this case- and giving it to those who borrowed the money, the borrowers. So, we have effectively charged interest on the banks, before they did it to us. You as an individual, and I might have not wanted to do it, but we live in a society which does it on our behalf, and when we use the money, we are implicitly agreeing to it. If you don’t like it, don’t use the money. Go to a country which doesn’t use money. There is no such country today. And if you use the money, you are part of the system, and you have effectively charged interest on the banks first. Maybe not intentionally, but that does not change the fact that it happened under your watch, being one of the rulers in a democracy. Of course, because for you as a submitter, it was unintentional and unavoidable, God will forgive you for this unwanted situation, as I explain in another video titled “The Global Forced Behaviour”. But the fact is, we effectively did charge interest on the banks first.
Now, when we go to get loans from banks, the banks make sure that they charge us a higher interest then we charged them so that they can make a profit. However, at least part of it, part of their interest, as you can see is just the cancelation of our interest on them. So, that part is not really true interest. It’s just the cancelation of your interest. So, because we unfairly took from them, if they also take from us up to that same amount, that is fair, and just. The Quran says, “an eye for an eye” and that’s allowed. But, as I said, the banks actually charge us more than what we charged them. So, what about that additional portion? Is that portion prohibited interest? Now that additional portion consists of two sub-portions:
The first sub-portion of the interest, even though it is called interest, it is effectively a fee which the bank charges, not for the loan, but for the services it provides connected with that loan. See, in the first example of how it worked in the past, where you went to a friend to get a loan, you would be doing all the work- you go to his home, you might or might not find him, so you might have to go to 5 friends before one of them actually has the gold coins, and maybe that money might be available, but maybe he needs it, so he can not give it to you. In that case, you are going through all the work, and the risk , and the inconvenience, and your friend is not providing you any additional service except for the loan. But, imagine if that friend said, let me actually open an office close to you, and hire some employees, and make sure that they stay there all day for you, only so that when you need a loan once in a while, we are there to serve you. That service would cost. You didn’t just get a loan, you got the loan and a service, the convenience of finding it whenever you need it, the technology involved to make it easier for you, through online services, cards and things like that. It’s the same when you order ice cream at a restaurant, for example. It is more expensive then when you buy it from the shop. It’s because you are not only getting the ice-cream. You are also getting the service. They put it nicely on the table for you. They’ll wash the ice cream bowl for you, afterwards. All of that service, of course, costs. People are staying away from their families, so they can be at your service. So, a portion of the interest which banks charge is not interest at all. It’s a service fee for the costs which they have to go through to serve you.
Now, the last portion of interest, the portion which is neither interest cancellation, neither a service fee, that portion is true prohibited interest – riba.
Now, the question is, how big of a portion is that? How much of the so-called interest which the bank charges you is actual prohibited interest, riba? And thankfully, it is easy to calculate, because banks get almost all their revenue from interest. Their total interest is pretty much their revenue, and their total expenses are all for services and the cancelation of interest which they had to do. So, this means that to calculate the remaining prohibited interest after service fees and cancelation of interest, all we have to do is calculate the remaining revenue after expenses. And if you are an accountant, you know that revenue minus expenses equals profit. So, the profit of the bank is exactly the prohibited portion of interest, the riba. So, when it comes to banks, not everything they charge you is riba (prohibited interest). Only their profit portion is “riba” (prohibited interest). And how much is that? Well, on average, the owners of banks have a profit margin of about 15% after taxes and inflation adjustments. So, only about 15% of the interest which the bank charges you is actually riba, the interest which is prohibited in the Quran. This means that if someone says that bank interest is prohibited in the Quran, they are about 85% wrong. And in the future, they will be even more wrong, because true business profits will gradually go down close to 0% just before the End of the World, but that’s another issue. But today, in 2025, bank interest is about 85% allowed according to the Quran, and about 15% prohibited.
Now, the question is. Should we avoid bank loans completely, just because only 15% of that deal is prohibited? And we can not separate the allowed portion from the prohibited portion, because they come together within the same loan. Well, we have two choices here. We can avoid bank loans, or we can decide to use them, and then atone for the prohibited portion through Penalty Zakat. And this is an option which is allowed in the Quran. In Sura 9, verses 102 and 103 tell us that if someone engages in mixed deeds, which include both good and sin them, then we should compensate for the sinful portion with charity, which I have labeled “Penalty Zakat”, because it is obligatory charity as penalty for your sinful portion of the deed. Now, knowing that bank interest is about 15% sinful, in another video I explain the details why we have to pay 7.5% of the sinful portion. So, 7.5% of 15% is about 1%. So, if you work in a bank, you have to give 1% of your income as Penalty Zakat, unless the owner of the bank gave it, but that’s very unlikely, so you have to give it. And if you own stocks of a bank, you have to give 1% of the profit unless the employees of the ban gave it, but that’s very unlikely, so you have to give it. But, if you just take a loan from a bank, you were already financially penalized by the bank through the slightly higher interest rate than you deserved to be charged, so you don’t need to pay penalty zakat for loans which you get from a bank.
However, just because it is permissible to get a loan from a bank, that doesn’t mean that you should. Just because something is not a sin, that doesn’t make it a smart decision. So, let me give you a friendly tip on how to be smart with loans. There are two types of loans: Consumption loans and investment loans. Consumption loans are for example, a loan to cover your wedding expenses, or a loan to go on vacation, or a loan to refurnish your kitchen, or a loan to buy a bigger house, because it just looks better, or a loan to get the newest PlayStation, or a loan to buy the more expensive car than you have the money for because it just looks better. These are consumption loans. Investment loans are loans for a new business, materials for your business, or to buy a basic car because you need it for work, which makes it an investment in some ways, because it enables you to earn money at work. So, if you want to be smart about loans, avoid consumption loans, and take investment loans, when you have a very good investment idea, of course.
Mortgages are between consumption and investment loans, because they are essentially a consumption loan, where the investment component is just as big, because it enables you to escape out of the situation of paying rent.
Now, credit cards are generally consumption loans, so when you have to use them because they make transactions easier, always make sure to pay them as early as possible, before the interest kicks in. One of the best ways banks take advantage of greedy and financially stupid people is through credit cards, because they have among the highest interest rates.
Now, in a democratic country, with free markets, banks compete against each other to offer the lowest interest rates on investment loans, and the investors are only willing to take those loans, if their interest rates are lower than what the expected return on investment would be. This means that in in true democracies, average bank interest rates are forced to be lower than the average return on investment. And the economy of a truly democratic country has never grown more than about 20% per year. You can only get that rate of growth in a non-democratic country, or a country which just came out of devastating war, which is not a democracy either. So, because in practice, it has never happened for a truly democratic economy to grow faster than 20%, then having bank loans with a higher interest rate than about 20% can only happen in a country which is practically not a democracy. And in that environment the interest rates are prohibited, because as we said in the beginning, for interest rates not to be prohibited, they have to happen in a democracy, through banks (not through people), and with fiat money (not with gold and silver).
Now, if you get a loan from an actual person, not a bank, then all interest is riba (prohibited interest). However, because we use fiat money (paper money), which has an unfair inflation attached to it, because the government keeps stealing it’s value by about 2 to 3% every year on average, then you are allowed to adjust for that inflation during that period. And if there is deflation, which is very rare, you can also adjust for deflation. Think of it like this. If a person loaned 100 sheep to his friend. Of course, he should return 100 sheep back. Any other number would be prohibited interest, “riba”. However, if while he held the sheep, he starved the sheep so much so that now they are 10% thinner. He can not come and say that because he received 100 sheep and he returned 100 sheep, that is fair. No, it’s not fair. Look at the sheep. They look like goats. You either bring the sheep as healthy as they were, or if you returned them 10% thinner, then the fair thing to do is to return 110 sheep. And the same with money. Inflation makes the money thinner, with less value, just like in the case with thinner sheep. So, it’s unfair if you don’t take inflation into account, for any loan which extends one year or longer, where inflation matters. And this has nothing to do with ribba. You are just making it fair. The same real value for the same real value.
Friday Sermon by: Alban Fejza, Online Congregation Director
Masjid Tucson
Masjid Tucson was a private house at 739, E 6th St, Tucson, Arizona, which Rashad Khalifa rented out from a private owner to enable the Friday gatherings of submitters back in the 1980s. Around 20 people would gather there every Friday to listen to Rashad Khalifa’s sermons in the 1980s. After Rashad Khalifa, it was abandoned, and now is simply a private home and the submitters do not gather to pray there anymore. Today, after the internet, the submitters are thinly spread throughout the world, and because any particular location does not have more than 100 of them, for practical purposes, instead of building a mosque, for the time being, they gather online through this website.
For more information:
Can We Do Friday Sermons Online?
Join us to listen to our online Friday meetings every Friday.
List of Articles About Rashad Khalifa
List of Articles About Alban Fejza
What is Muhtasib (Market Inspector in Islamic Governance)?
Muhtasib refers to an official responsible for ensuring that markets, trade, and public transactions adhere to Islamic law, ensuring fairness and preventing fraudulent activities.
Key Aspects of Muhtasib:
- Market Regulation: The muhtasib oversees commercial transactions, ensuring that merchants are honest, weights and measures are correct, and that no unlawful goods are sold.
- Public Morality: The muhtasib ensures that public morals and Islamic values are upheld, preventing immoral behavior or indecency in the marketplace.
- Enforcement of Justice: They have the authority to intervene in disputes, punish dishonest traders, and ensure that Islamic principles govern public life.
Importance of Muhtasib:
- Ensuring Fairness in Trade: The muhtasib ensures that markets operate on principles of fairness and honesty, protecting consumers and promoting ethical business practices.
- Upholding Islamic Values: This role helps maintain public morality and discipline, ensuring that public spaces and commercial activities align with Islamic ethical standards.
- Promoting Social Welfare: By regulating markets and ensuring compliance with Islamic law, the muhtasib contributes to a stable and just economic system that benefits the wider society.
Written by AI. A more correct, God given, explanation can be found here.
What is Bayt al-Mal (Treasury of the Islamic State)?
Bayt al-Mal is the state treasury in an Islamic governance system, responsible for managing public funds, including revenues from taxes, zakat, and other sources. It ensures the distribution of wealth in accordance with Islamic principles of fairness and justice.
Key Aspects of Bayt al-Mal:
- Collection of Funds: Bayt al-Mal gathers resources through taxes, zakat, and other lawful sources, intended to support the welfare of the Muslim community.
- Economic Management: It oversees the distribution of funds to meet the needs of society, including welfare, public services, and maintenance of public infrastructure.
- Social Justice: The treasury is a key instrument for ensuring the equitable distribution of wealth, particularly focusing on poverty alleviation and social welfare.
Importance of Bayt al-Mal:
- Ensuring Justice and Fairness: Bayt al-Mal plays a critical role in Islamic governance by ensuring wealth is distributed justly and used for the welfare of all citizens, particularly the underprivileged.
- Fostering Economic Stability: It serves as the backbone of the state’s financial system, ensuring funds are effectively managed for the greater good of society.
- Promoting Social Responsibility: By managing funds according to Islamic law, Bayt al-Mal promotes social responsibility, reinforcing the Islamic values of charity, fairness, and care for the vulnerable.
Written by AI. A more correct, God given, explanation can be found here.

